Differences Between an El Niño and La Niña and How They Can Affect Your Fishing
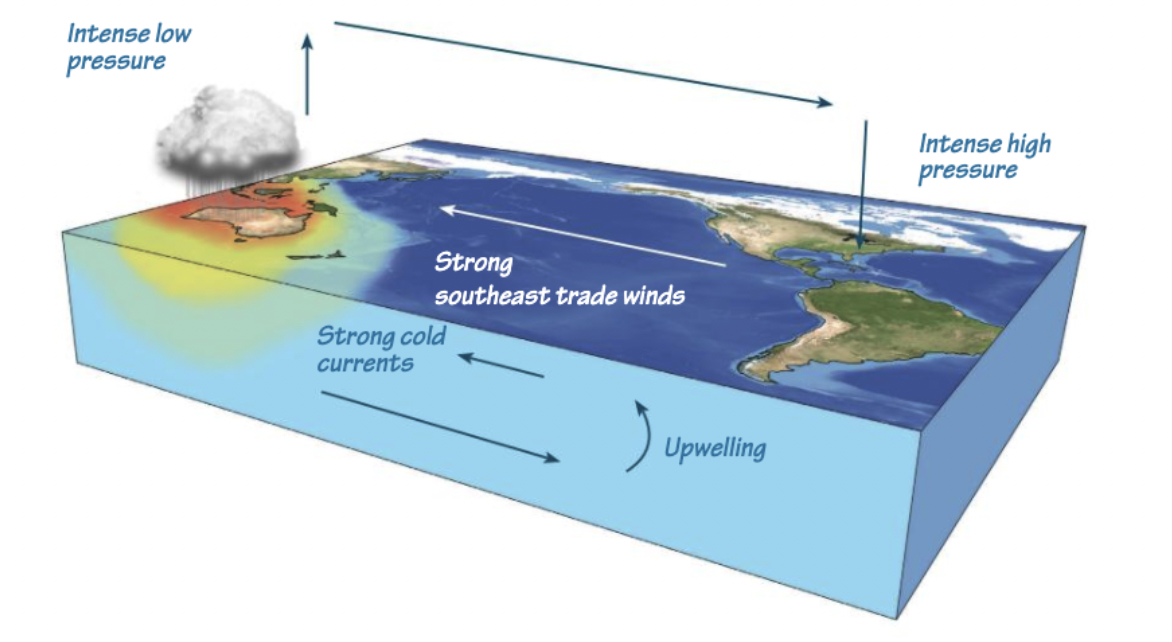
El Niños and La Niñas are global weather phenomena that typically happen once every 2 to 7 years. El Niños usually occur much more than La Niñas. Weather patterns in the United States are a result of the global wind patterns. El Niños and La Niñas directly affect the international trade winds, which are winds that blow from east to west from the poles to the equator. These standard wind patterns are what directly cause the weather patterns we typically see: cold and wet winters in the north, dry and warmer winters in the south. However, El Niño slows down and sometimes reverses these trade winds. This leads to warmer and hotter winters in the north, and colder and wetter winters in the south. A La Niña intensifies the typical wind patterns.
So what does this have to do with fishing? As we all know, snowpack affects water levels in fly fishing streams. During an El Niño, the snowpack will be far below average. This means that prime water levels will occur earlier than usual, as there will be less snow. This also means that there is a genuine drought concern later in the fishing season. This means that an El Niño is detrimental to fishing because it disrupts spawning, making it difficult for fish populations to remain stable.
The exact opposite can be said for a La Niña. A La Niña will cause there to be more snow in the north, leading to a much larger snowpack. This means that water levels will become prime much later in the season. There can also be a significant flood risk early in the season. A general sentiment is that this is better for fish populations because there are more nutrients in the water as a result. This can lead to healthier and larger fish, resulting in increased fish reproduction.
It is essential when planning a fishing trip in the Northern United States to see what weather patterns are occurring. Knowing and predicting a location's snowpack can be very beneficial to your ability to catch fish.